45 plastids diagram with labels
History of botany - Wikipedia Diagram showing the sexual parts of a mature flower It was Rudolf Camerarius (1665–1721) who was the first to establish plant sexuality conclusively by experiment. Plastids: Everything You Need to Know and More - Microscope Clarity Plastids are a diverse group of double-membrane bound organelles found in most plants and algae. They may also be found in ferns, moss, parasitic worms and marine mollusks. Apart from photosynthesis, these organelles also assist in food storage and synthesis of compounds such as lipids, amino acids and carbohydrates.
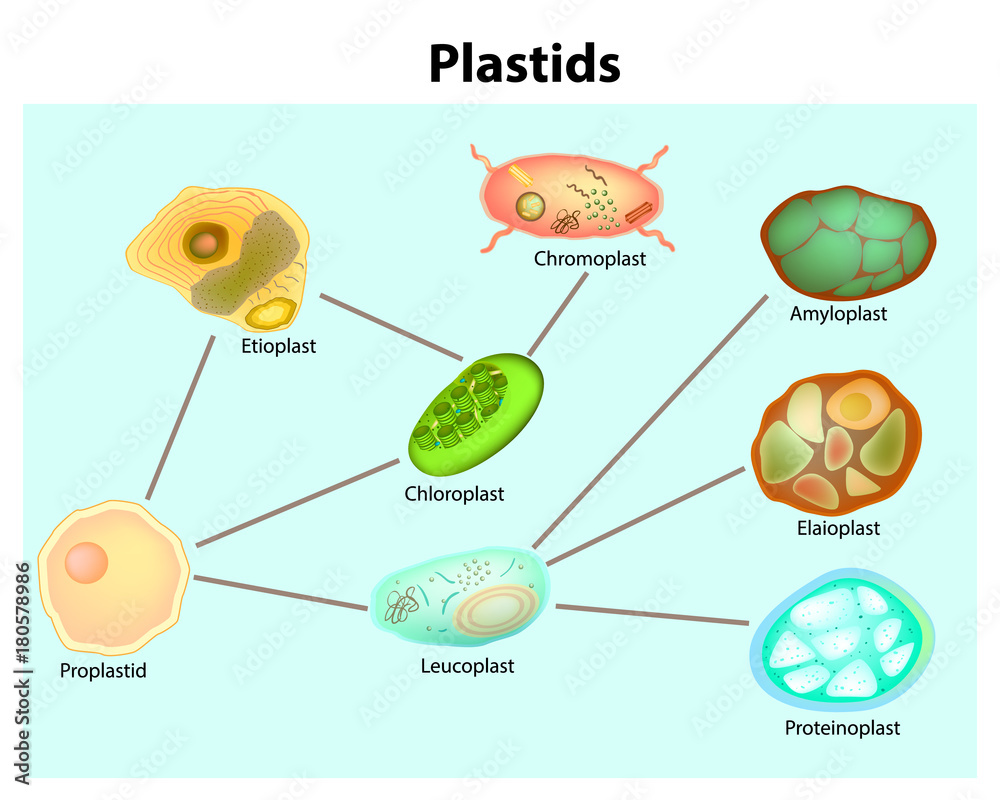
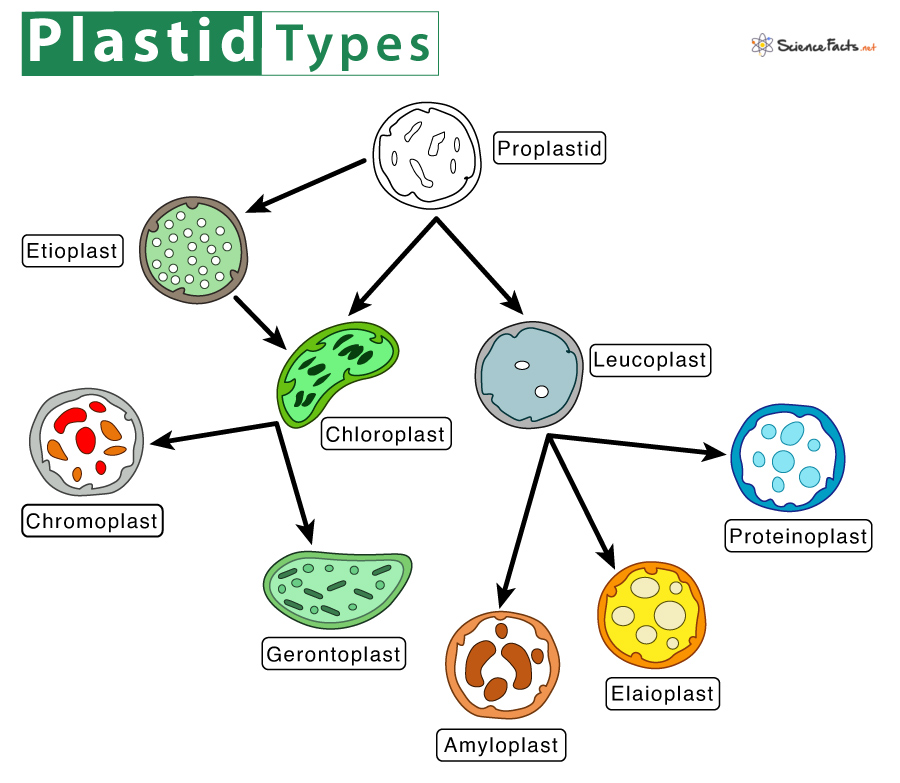
Study Notes on Genetics of Plastids (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion In the cytoplasm of the plant cells are found many small cytoplasmic bodies, called plastids. These plastids are of several types, such as, chloroplast, leucoplast, chromoplast and so on. Plastids arise from smaller particles, the proplastids, found in the egg cytoplasm. They reproduce themselves independently of other cell parts by process of ...

Plastids diagram with labels
Plastid - Wikipedia Plastid. Plant cells with visible chloroplasts. The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded - plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle [1] found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Examples include chloroplasts (used for ... Plant Cell: Definition, Types of Plant Cells and More - Embibe Plastids in Plant Cell They are membrane-bound organelles that have their own DNA. They are necessary to store starch, to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is also used in the synthesis of many molecules, which form the building blocks of the cell. Based on the type of pigment, they are of Plastids are of three types: a. Mitochondria diagram - lyb.tt-milk.info Diagram Of Mitochondria The diagram below shows the structure and functions of the mitochondria. Structure and Functions Of Mitochondria Matrix It is a viscous or gel-like fluid containing a mixture of enzymes, ribosomes, inorganic ions, mitochondrial DNA, nucleotide cofactors, and organic molecules. DNA. Functions. Disease. Aging.
Plastids diagram with labels. bio 1407 exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Label the image below to describe the basic structures of a virus., Types of viruses Label each of the following images to describe four different types of virus., Unique characteristics of viruses Viruses are considered a bit of a biological enigma because they have characteristics of living organisms, but not all of these ... Structure and Function of Plastids in Plant Cell - NotesHippo Plastids in plant cell are the sites where key chemical compounds utilised by autotrophic eukaryotes' cells are manufactured and stored. 3. All of the enzyme components required for photosynthesis are found in the thylakoid membrane. Within the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll interacts with electron carriers, coupling factors, and other ... Parts of plant cell - lksz.schoenbergmusikanten.de Golgi 7. apparatus 8. ribosomes 9. plastids 10. mitochondria 10. vacuoles ... Plastids - is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. A plant is made up of many different parts. The three main parts are: the roots, the leaves, and the stem. Chloroplast - Wikipedia A chloroplast / ˈ k l ɔːr ə ˌ p l æ s t,-p l ɑː s t / is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells.The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells.
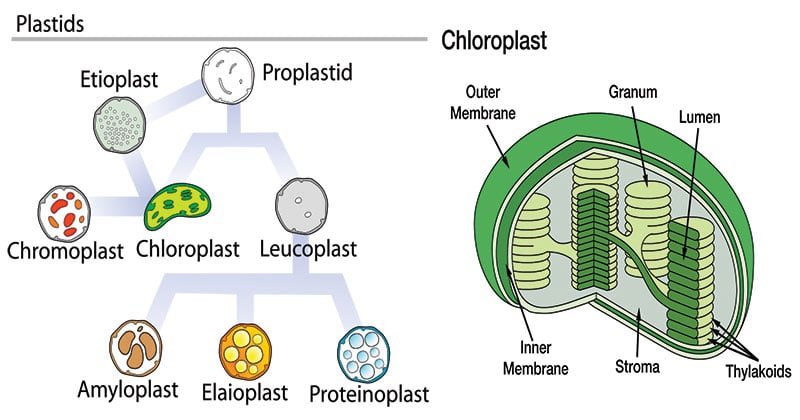
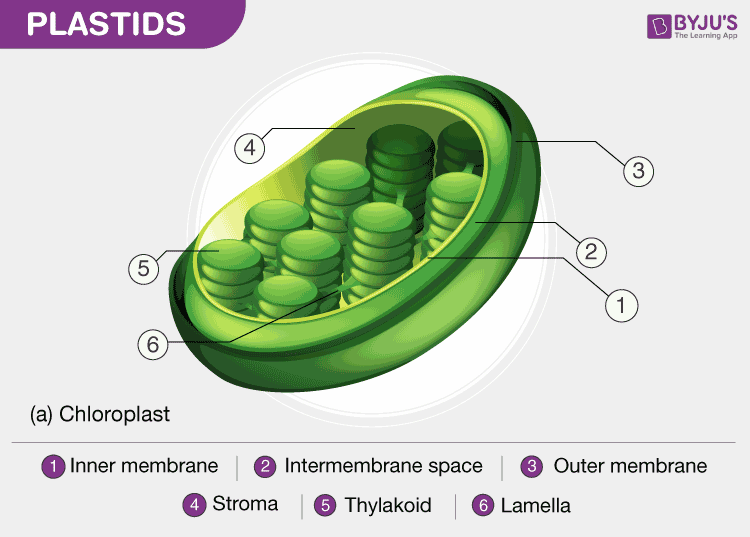
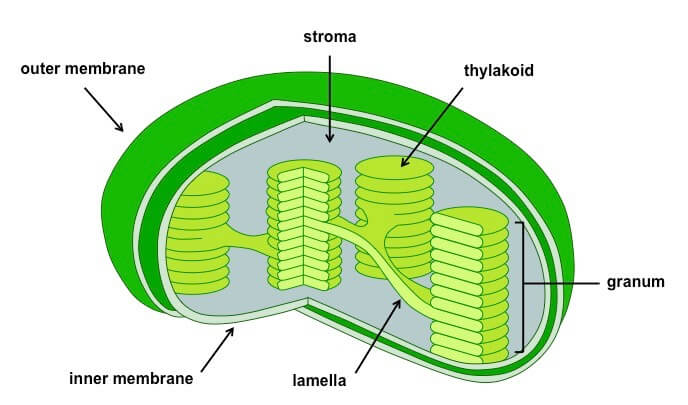
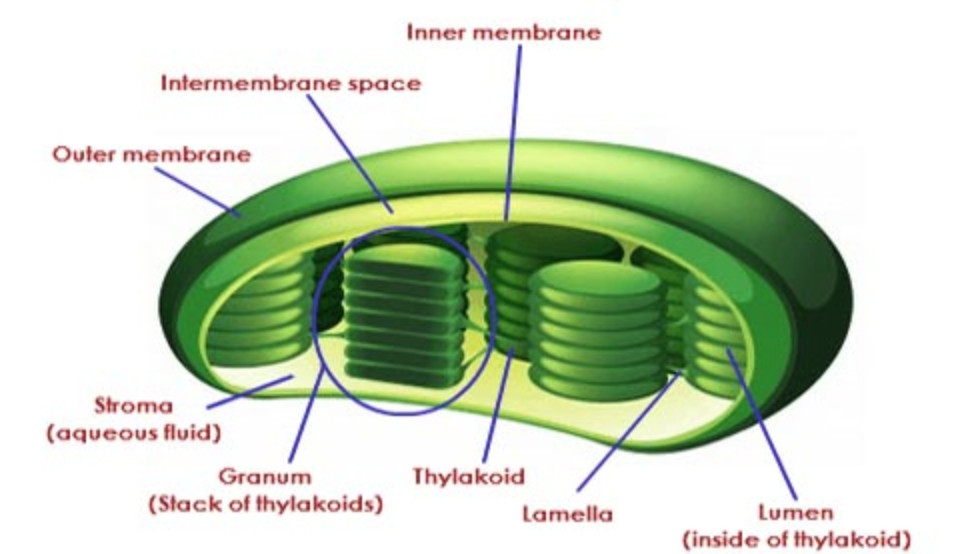
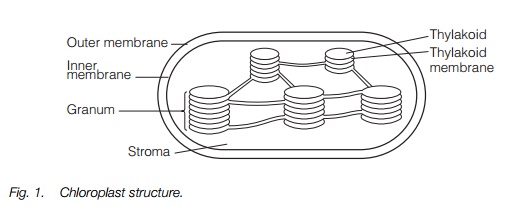
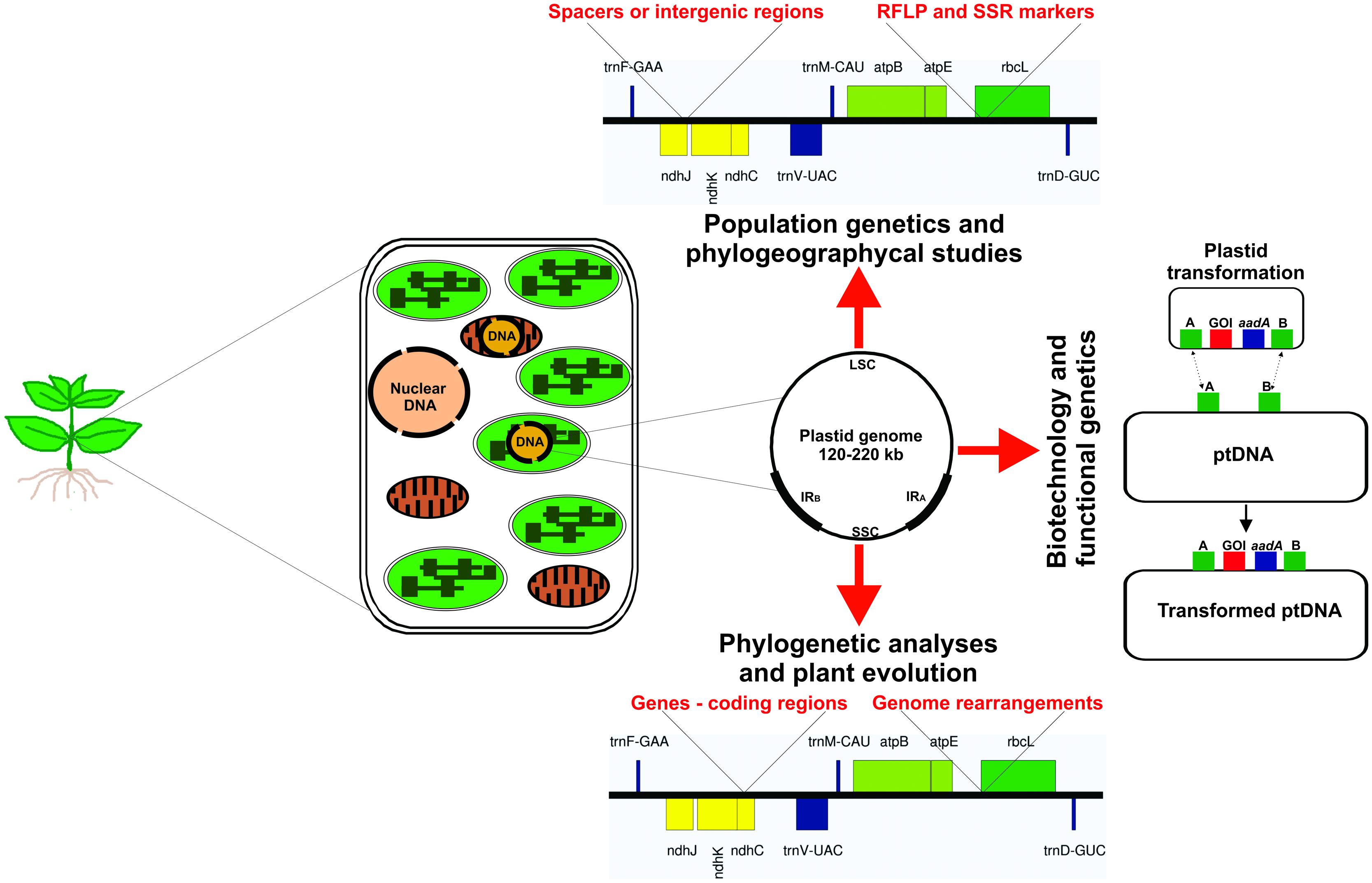
Gene Help: Integrated Access to Genes of Genomes in the ... Sep 13, 2006 · The gene being shown on the diagram is in maroon. All other diagrams and labels anchor links to specific Gene pages, supporting quick navigation to review neighboring genes by clicking in the area of the symbol/arrow. The diagram shows the gene’s placement on any and all chromosomes in the current genome annotation. Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast - BYJUS The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid membrane, stroma and lamella can be clearly marked out. Chloroplast Diagram representing Chloroplast Structure Plant Cell Diagram Plastids : Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts ... Labeled diagram of plant cell, created with biorender.com. Plastids & its Types, Function, Structure - BioMD from biomd.in A diagram of a plant cell. Like all organisms, plants have cells. But in some ways they are different from animal cells and the cells of other eukaryotes. Click here for a labeled diagram of this cell. Structure of 3-oxoacyl-(acyl-carrier protein) synthase II ... May 01, 2008 · The amino-acid sequences of KAS I and KAS II share 38% identity and their functions are closely related, catalyzing the condensation of acyl-ACP with malonyl-ACP. In plastids, KAS I extends C 4 in the substrate to C 16 in six rounds of elongation, whereas KAS II carries out an additional step to give a C 18 product (Olsen et al., 2001 ).
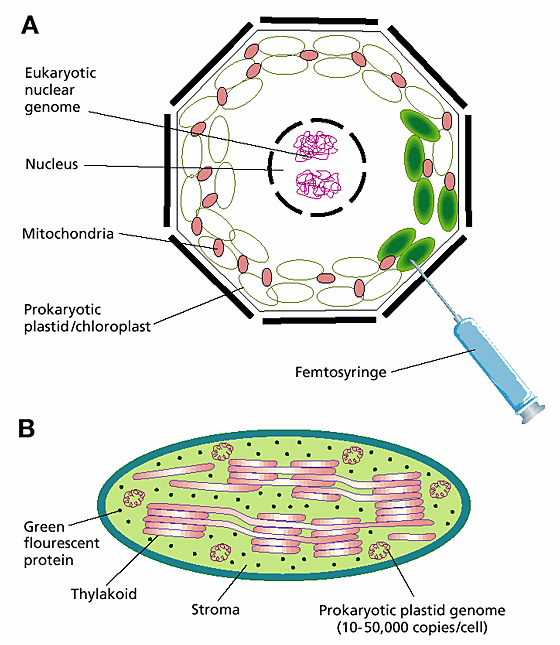
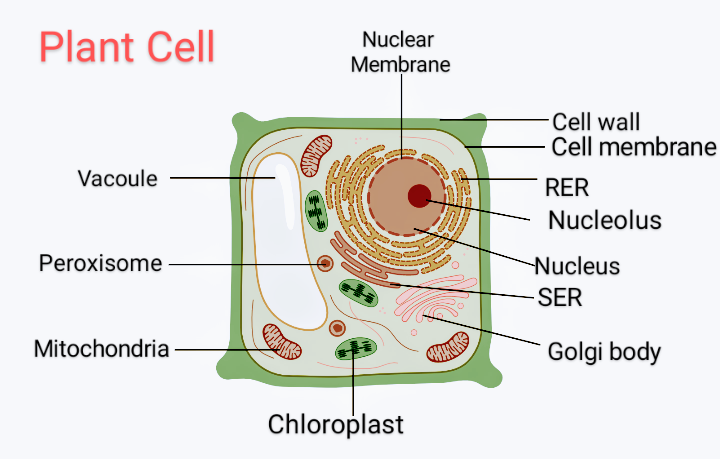
Labeled Plant Cell With Diagrams | Science Trends The parts of a plant cell include the cell wall, the cell membrane, the cytoskeleton or cytoplasm, the nucleus, the Golgi body, the mitochondria, the peroxisome's, the vacuoles, ribosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum. Parts Of A Plant Cell The Cell Wall Let's start from the outside and work our way inwards. Plastids: Types, Structure and Function (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Plastids may be coloured or colourless and are of three types. The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids principally serving the purpose of storage. On the basis of nature of storage compound, leucoplastids are amyloplasts (starch), elaioplasts (oil) or aleuroplasts (protein). The green plastids or chloroplastids are needed for photosynthesis. Plastids - Definition, Types, Main Structure and Function Studies have also shown the plastid to be polarized and ranging from 5 to 10 micrometers in width depending on the plant. Like the other plastids, chloroplasts have a double membrane envelope consisting of the outer and inner membrane (phospholipid layers). The space within the double membranes is covered with an aqueous matrix known as stroma. Localization and distribution of YFP-labeled plastids in elongating ... Download scientific diagram | Localization and distribution of YFP-labeled plastids in elongating pollen tubes. (A) Plastids in pollen tubes of ACT1p::TP FtsZ1-YFP plants. YFP fluorescence or ...
Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The chloroplasts are the cell organelles which consist of these pigments. The 3 types of pigments present in plants are chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins. Chlorophyll imparts the green color to plants. Plastids are membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles that can be found in the cells of plants and algae.
Plant Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet The cell wall is made of cellulose and lignin, which are strong and tough compounds. Plant Cells Labelled Plastids and Chloroplasts Plants make their own food through photosynthesis. Plant cells have plastids, which animal cells don't. Plastids are organelles used to make and store needed compounds. Chloroplasts are the most important of plastids.
Draw A Neat Diagram Of An Animal Cell And Label The Following ... Label the parts neatly as shown. Structure formed of two centrioles arranged in a perpendicular manner. Except the protozoan euglena no animal cell possesses plastids. Asked nov 28, 2017 in class ix science by ashu premium (930 points). Labelled diagram of animal cell. 3.draw cell organelles as shown. Labelled diagram of animal cell.
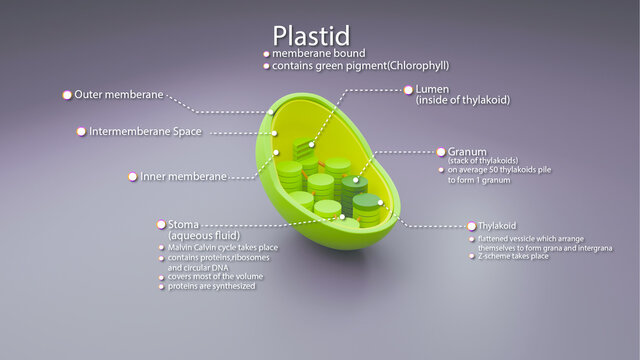
Plastids: Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram All kinds of green plastids are found to be surrounded by two membranes, these are inner and outer and are 7 nm thick membranes. They are separated by an 8-10nm thick periplastid space. A fully developed plastid's inner membranes do not have any inward foldings, unlike Mitochondria. Structure of Plastids Inheritance of Plastids
Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram Plastid is a double membrane-bound organelle involved in the synthesis and storage of food, commonly found within the cells of photosynthetic plants. Plastids were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, but A. F. W. Schimper was the first to provide a clear definition.
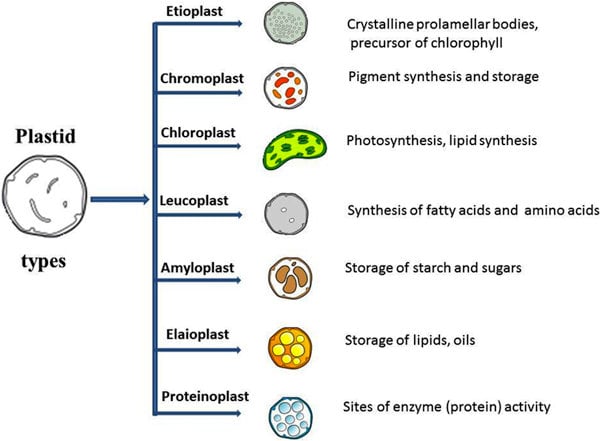
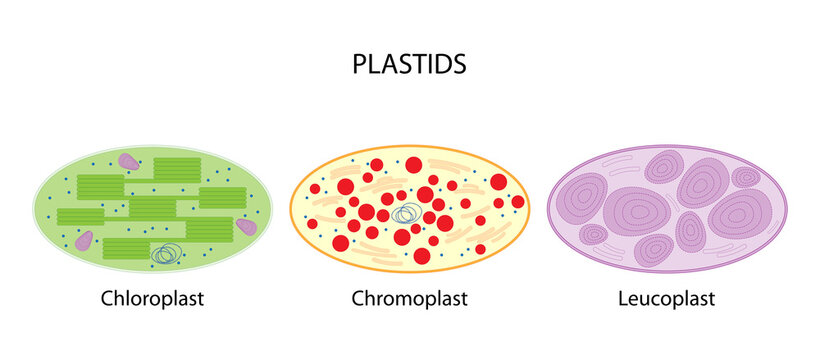
Plastids: Definition, Types, Function - Embibe Types of Plastids and Functions of Plastids Plastids are further divided into 3 types that have different functions and some have biological pigments as well. 1. Leucoplasts 2. Chromoplasts 3. Chloroplasts Leucoplasts These colourless Plastids possess internal lamellae and do not contain photosynthetic and grana pigments.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Figure: Labeled diagram of plant cell, created with biorender.com The typical characteristics that define the plant cell include cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin, plastids which play a major role in photosynthesis and storage of starch, large vacuoles responsible for regulating the cell turgor pressure.
Plant Cell-Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Figure: Labeled diagram of a plant cell, created with biorender.com The plant cell is comprised of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, as well as plastids, which are essential for photosynthesis and starch storage, and enormous vacuoles that control cell turgor pressure.
Plastids - Different types of Plastids and their functions in ... - BYJUS There are different types of plastids with their specialized functions. Among them, a few are mainly classified based on the presence or absence of the Biological pigments and their stages of development. Chloroplasts Chromoplasts Gerontoplasts Leucoplasts Chloroplasts
Mitochondria diagram - lyb.tt-milk.info Diagram Of Mitochondria The diagram below shows the structure and functions of the mitochondria. Structure and Functions Of Mitochondria Matrix It is a viscous or gel-like fluid containing a mixture of enzymes, ribosomes, inorganic ions, mitochondrial DNA, nucleotide cofactors, and organic molecules. DNA. Functions. Disease. Aging.
Plant Cell: Definition, Types of Plant Cells and More - Embibe Plastids in Plant Cell They are membrane-bound organelles that have their own DNA. They are necessary to store starch, to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is also used in the synthesis of many molecules, which form the building blocks of the cell. Based on the type of pigment, they are of Plastids are of three types: a.
Plastid - Wikipedia Plastid. Plant cells with visible chloroplasts. The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded - plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle [1] found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Examples include chloroplasts (used for ...



























Post a Comment for "45 plastids diagram with labels"